Cannabis is one of the oldest and most versatile crops known to humanity. The species Cannabis sativa specifically has had a long and extensive history entwined with our own, and is commonly classified by its chemical components into either hemp or marijuana, depending on how psychoactive the individual strain is.
This division is based on the plant’s cannabinoid levels. Cannabinoids are chemical compounds found in cannabis (after which they are named), as well as some other plants and almost all vertebrates (animals with a backbone). The two most prominent of these are CBD and THC, though there are over 100 others, and likely more as researchers dig deeper into cannabis profiles. For a more in-depth exploration of these molecules, check out our article on phytocannabinoids.
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the psychoactive component of cannabis, and is responsible for the characteristic “high” of marijuana. Thus, it provides the defining line between hemp (which has less than 0.3% THC and so is not intoxicating) and marijuana (with more than 0.3% it has a psychoactive component, and remains illegal in many states).
Which brings us to CBD, which stands for cannabidiol, a molecule present in both hemp and marijuana; though in the latter it is often overshadowed by its more sensationalized cousin THC. Marijuana has been bred throughout the years to induce a stronger and stronger high. So THC content in cannabis has been artificially selected for, and CBD, with it’s much more subtle effects, has often been unintentionally bred to much lower levels.
In hemp, however, CBD is the star player, and it is by far the most prominent cannabinoid found in the plant. First and foremost, since CBD is non-intoxicating, it will never get you high, and it was federally legalized in December of 2018, after nearly a century of prohibition. Even more importantly, both modern research and traditional folk medicine show that CBD may greatly benefit the animal body by maintaining, protecting, and repairing our health and homeostasis.
Our bodies contain a signaling network called the endocannabinoid system. It is one of the largest systems in the animal body in both size and scope, and it functions by using neurotransmitters (called endocannabinoids), along with their receptors and enzymes, to maintain balance, or homeostasis, within an organism. Phytocannabinoids (cannabinoids produced by plants, like CBD) effectively mimic the structure of our own endocannabinoids, and work within this system to regulate an astoundingly wide and seemingly unconnected array of health and wellness issues that affect nearly every aspect of our lives. Read more about this fascinating system here.
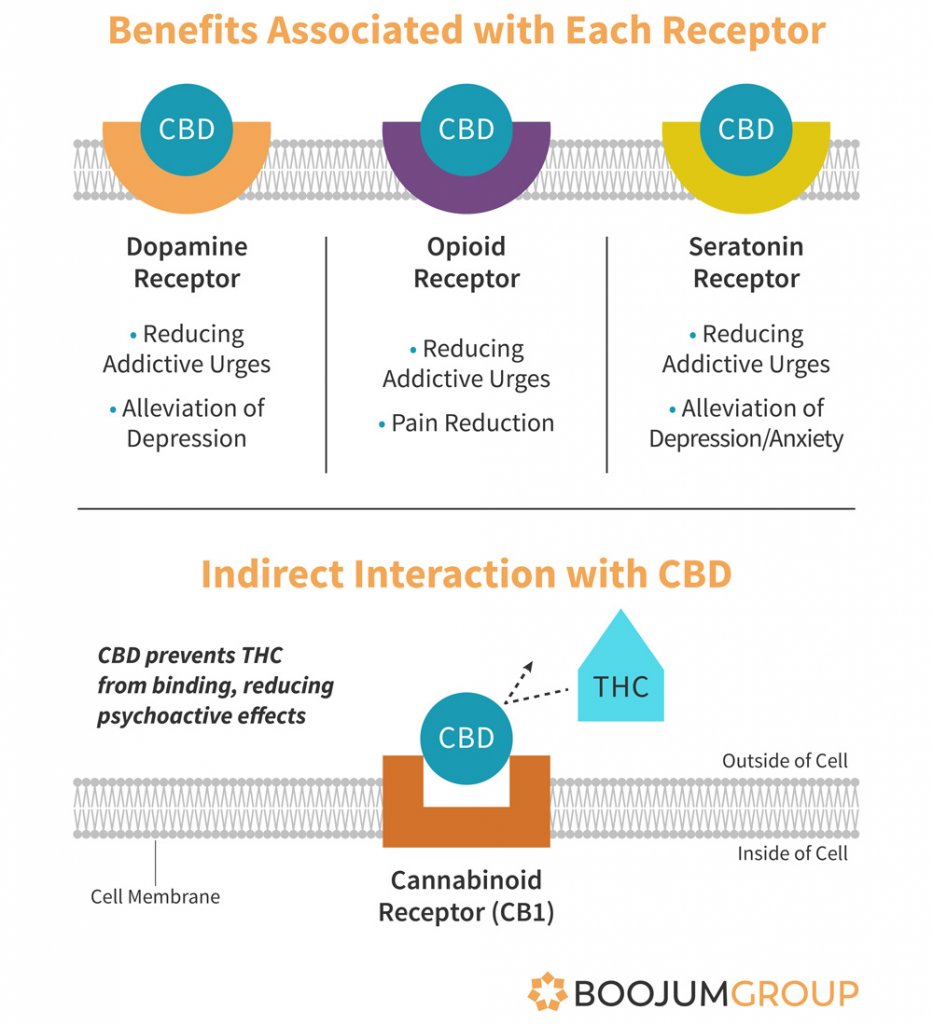
In addition to affecting the receptors and enzymes within the endocannabinoid system, CBD has been shown to interact with opioid, dopamine, and serotonin receptors. While there is a dearth of research on how exactly each of these interactions affect the human body, there is a growing body of evidence showing CBD’s ability to regulate pain, dampen drug cravings and withdrawal symptoms, and decrease depression and anxiety – all of which are regulated by these receptors.
Additionally, while CBD does not directly activate the endocannabinoid receptor, CB1, it does interact with it, and actively blocks THC from activating it. This means that CBD effectively works as an antidote to THC, blocking its psychoactive effects. Without a receptor to bind to, the THC is incapable of producing its characteristic high. Thus taking CBD can be a good antidote to marijuana psychoactivity, as the CBD molecules compete with THC for available receptors. It also helps to explain the low levels of CBD present in many strong marijuana strains – genetics with higher levels of CBD may dampen the high of the THC, and so have been bred out of high potency product.
The therapeutic effects of CBD are varied and numerous, each backed by different levels of evidence – from anecdotal stories to extensive research and clinical trials. While cannabis has been used as a painkiller as far back as 2900 BC, perhaps one of its best-known modern uses is as an anti-seizure medicine, especially effective in the treatment of childhood epilepsy.
A continually increasing number of scientific studies are looking at CBD and its role in healing. It has exhibited signs of being neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, anti-spasmodic, anti-tumoral, anti-psychotic, anti-nausea, and analgesic (pain relieving), and shows promise in the treatment of insomnia, PTSD, ADHD, addiction, Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis, heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, tissue healing, and more. What side effects have been observed are mild, including diarrhea and fatigue, with one study suggesting adverse effects on the liver.
CBD can be applied topically (as an oil or salve) or ingested via inhalation (of smoke or vapor), eaten, or absorbed under the tongue. Laws are still evolving and being drawn around the country and continent, so it is important to find out which modes of consumption are legal where you live. Beyond that, it all comes down to personal preference. While CBD itself is tasteless as an isolate, it is becoming more and more evident that its benefits are greater and more far-reaching when it is left in combination with other cannabinoids and occasionally terpenes (plant molecules with purported health benefits and characteristic aromas) in a full spectrum oil. When these compounds are allowed to interact, the “entourage effect” comes into play, and their synergy increases the efficacy of this whole plant medicine.
The nascent CBD industry is still finding its footing regarding regulation and oversight, so if you decide that CBD might be right for you, make sure to find a reputable company whose products you trust. A review conducted by the University of Arkansas of over two dozen products containing CBD found that virtually none of them had cannabinoid levels matching their claims, and that some even included synthetic (rather than plant-derived) CBD, or none at all. Make sure that any company you purchase from can provide proper licensing and third-party testing results to ensure that you know exactly what you are getting – both in terms of quality and dosing accuracy.
Given a known amount of a quality product, CBD’s potential is clear – its possibilities have energized the research and medical communities, and its stratospheric rise in public opinion attests to the fact that it’s doing something right. If you have any questions about CBD or our products, please get in touch – we love to hear from you!
